PREVENTION
Ticks: Reasons to Fear
A Tick Bite Can Kill You

One tick can transmit multiple infectious diseases in a single bite. They can be carriers of many diseases at once.
Ticks are arachnids (not insects) & have 8 legs. They are related to spiders & mites. Ticks are parasites that feed on the blood of humans & other animals in order to survive. They feed on a variety of animals, including birds, mammals, reptiles, & amphibians. They are considered disease vectors (carriers). After feeding on a Lyme disease-infected animal (usually a mouse or other rodent), they carry & transmit the Lyme pathogen (primarily Borrelia burgdorferi) to the animal or person that is their next meal.
There are over 800 different types of ticks around the world. Lyme disease is transmitted via black-legged ticks. You do not need a deer population near you to have Lyme infected ticks or to get Lyme disease. This is a misconception based on the name of one tick species; in addition, all black-legged tick species spread Lyme disease & other tick-borne infectious diseases, not just the "deer tick." Other types of ticks also spread many dangerous tick-borne diseases.
The original hosts of the bacteria that causes Lyme disease are mice, short-tailed shrews & masked shrews, & chipmunks. Ticks pick up the bacteria from mice & other rodents when the ticks feed on them. One small mouse can carry up to 100 ticks.
Tick Season

Ticks are active year round & can even survive freezing temperatures. Their level of activity depends on climatic conditions & their peak season begins in April & runs through September, in temperate areas. During this time, the hungry nymph-stage tick (about as small as a poppy seed) actively seeks a blood meal, & its bite poses the greatest risk of disease transmission.
During winter months, when the ground is thawed & temperatures are above freezing, ticks are looking for food. Wearing protective clothing & doing daily tick checks must still be done during these warmer winter days.
Photo Credit: Tick Encounter Resource Center. Photographer Mary Holland
Tick Lifecycle
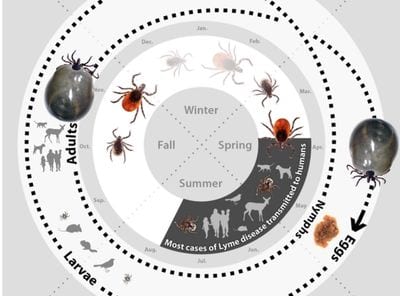
A tick life-cycle is two (or more) years. Ticks go through four stages of life (egg, larva, nymph, adult) & need to eat blood at each stage to survive and mature. Ticks survive winter; they hibernate by staying warm under layers of leaves & constant snow. On warm winter days, between snow melts when the ground is thawed & the outside temperature is above freezing, ticks venture out (so they can still be a risk during winter months).
Photo Credit: University of Rhode Island, Tick Encounter Resource Center
Tick Habitat

Many people think ticks are only present in the woods; however, ticks can be found in many areas:
- Where woods/fields meet lawn & garden
- Wooded areas
- Tall brush/grass
- Under leaves (to prevent dehydration) - leaf piles are a favorite of ticks
- Small numbers on cut/raked lawns or sports fields
- Under ground-cover (plants) in yard (to prevent dehydration)
- Around stone walls & woodpiles (where mice & other small mammals live)

Learn all about ticks & why you must be cautious every day, even in urban environments.
Tick Removal & Testing
PROPER TICK REMOVAL
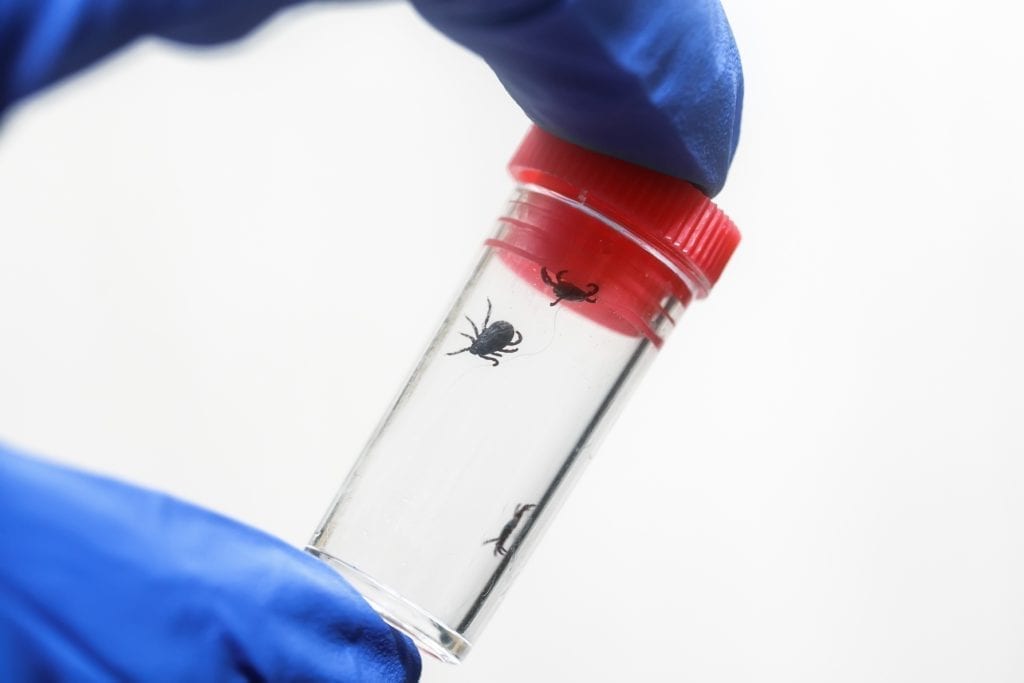
Do not panic if a tick is attached to your skin. Keep calm & remove it properly & promptly by following these steps below. By removing the tick as soon as you can, you reduce the chance of infection.
Using fine-pointed tweezers, grasp the tick at the place of attachment, as close to the skin as possible. By grabbing the body of the tick, you can squeeze more pathogens into your body & increase your risk of disease.
Gently pull the tick straight out with steady, even pressure. Do not squeeze, twist or jerk the tick. Doing so may break off the tick's mouth inside your body. Watch this video by a tick expert at the University of Manitoba on how to remove a tick.
Do not touch the tick with bare hands.
Place the tick in a zippered plastic bag with a moist cotton ball, write the date you found the tick on the bag, & bring it to your local health department (if they offer the service) or send it to a private lab for testing.
If a rash appears, take a photo & write down any symptoms you may have, & call/visit your doctor immediately.
Tick Testing Labs
This list below is provided as a convenience only. LymeTV is not affiliated with any of these labs in any way, does not provide funding to them or receive any payments from them, & does not recommend or endorse any of the labs or their tests above another.
Bay Area Lyme Foundation does free tick testing. We recommend this lab on the basis of cost & range of diseases tested. Reports are received about 12 business days after the tick is received at its lab. This lab is not currently accepting ticks. We will update when it begins again.
University of Maine Cooperative Extension: Tick Lab
17 Godfrey Drive
Orono, ME 04473
Phone: 207-581-3880
PA Tick Research Lab – Free for PA Residents
TickCheck Tick Testing, LLC – For non PA Residents
East Stroudsburg University Innovation
562 Independence Rd.
East Stroudsburg, PA 18301
Phone: 1-866-713-TICK
Tick Report – Subsidized for some MA towns
29c Cottage St.
Amherst MA 01002
Email: [email protected]
CT Agricultural Experiment Station
123 Huntington Street
New Haven, CT 06511
Phone: 203-974-8500
Upstate Tick Testing Laboratory – Free for NY Residents
Thangamani Lab
505 Irving Avenue, Syracuse NY 13210
4209 Institute for Human Performance (IHP)
SUNY Upstate Medical University
Email: [email protected]
Connecticut Veterinary Medical Diagnostic Laboratory (CVMDL) at UCONN
61 North Eagleville Rd., U-3089
Storrs, CT 06269
Phone: 860-486-3738
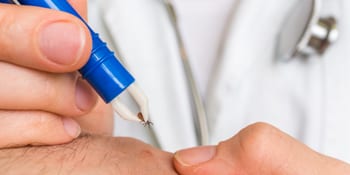
Properly removing a tick is vital; not doing so can increase your risk of disease.
Protect Your Neck
PROTECT YOUR NECK

It is vital to protect yourself daily from tick-borne infectious diseases, as well as other vector-borne infectious diseases, such as those transmitted by mosquitoes (the deadliest animal on the planet - killing almost 1 million people per year with vector-borne infectious diseases, globally). Here are simple steps that can reduce your risk of dangerous tick bites:
Wear bug repellent daily (EPA-Approved tick repellent, the active ingredient MUST be at 20% concentration or higher to be effective against ticks. Picaridin, DEET, IR3535). Essential oils do not protect against tick bites as it may for mosquitoes.
Treat your clothing, or purchase clothing treated, in permethrin (an insecticide).
Avoid areas of high grass, bush, & trees. If this is not possible, wear protective clothing.
Protective clothing means: socks over pants, long sleeves & long pants, & lightly colored clothing to be able to see bugs crawling on yourself more easily. You can also wear permethrin-treated mesh clothing between your skin & regular clothes, to give yourself an additional layer of protection from a tick attaching.
Daily tick checks are vital, especially in tick endemic areas. Remember, ticks are everywhere & you do not need deer to have Lyme disease. Mice & other rodents are the original hosts of the bacteria which causes Lyme disease. You can be in a non-rural setting & still get Lyme disease. Getting into the habit of daily tick checks is a great way to ensure that you are reducing your risk of these diseases, no matter your setting.
Do not forget to do daily tick checks on your pets. Pets can carry ticks into your home from outside, or even from your local veterinarian’s office. Pets can bring ticks into your home & into your bed, leaving you susceptible to a tick bite.
Once you get home, strip off all of your clothing & inspect all of your gear. Putting clothes in the dryer on high for at least 15 minutes will kill any ticks that may have hitched a ride.
Shower right away & do your tick check at that time. Also repeat the tick check before going to bed.
If you find a tick attached, remove it properly & save it with the date found, or send it off immediately to be tested for disease.
Protect your property with tick tubes. Watch our How-To Tick Tube video here. Tick tubes are biodegradable cardboard tubes stuffed with cotton soaked in permethrin. Mice, which can each carry up to 100 ticks on their body, take the cotton from the tubes to their dens to use for nesting. The cotton does not harm the mice; however, it kills the ticks on the mice. Tick tubes are a huge contributor to reducing the number of ticks on your property. Tick tubes work; tests have proven that the risk of encountering infected ticks on the treated property can be reduced up to 97% by the use of tick tubes. Here, you can find information on how many you need for your property & how they work on this FAQ about tick tubes. You may make them yourself, or you may purchase them already made on the Internet. LymeTV has no affiliation with this company in the link, nor do we receive any money from them; we only provide the information as a convenience to learn more about tick tubes.
High-Moderate Risk Activities for Tick Bites
High risk activities include any activity that exposes you to areas where ticks like to live, such as the woods, grassy or leafy areas, & beach grass. If you enjoy sitting in the grass for a concert, picnic, campfire, or to relax, take proper precautions to be tick safe. Remember ticks like moist, shaded areas. High-Moderate Risk Activities include, but are not limited to the following:
- Camping
- Hiking
- Walking on trails
- Off-road biking
- Hunting
- Fishing
- Golf
- Baseball
- Gardening
- Raking/Playing in the leaves
- Horseback riding
- Grass Cutting
- Walking your dog in a park
- Sitting in grass for picnics or relaxing
Pets & other outdoor animals increase your risk for a tick bite. Check your pets immediately when they come indoors. The simplest way to avoid tick bites is by avoiding direct contact with ticks. This can be easily done by avoiding wooded & bushy areas that have high grass & leaf litter. When walking through trails, walk in the center to avoid brushing up against grass or bushy areas. Always wear protective clothing & bug repellent. In addition, you can treat your clothing with an insecticide called permethrin, & wear mesh clothing between your skin & outer clothing to give added protection from a tick attaching to your body. Never forget daily tick checks!
A tick bite can kill you. Being informed of the dangers & effective prevention is imperative.

Prevention tips for yourself & family. Everyone is at risk for tick bites.
Pets
Pets

Both dogs & cats are susceptible to a variety of tick-borne illnesses, including Lyme disease. Pets may also bring ticks into your home & increase the risk of human infection.
Prevention is key to keeping your pets Lyme free. Here are some easy steps:
Keep your pet out of tick infested areas, such as tall grasses, wooded areas & marshy ground.
Keep your lawn well maintained.
Some topical products & tick collars help reduce risks by repelling &/or killing ticks.
If your pet has been outside, especially in a high risk area, check thoroughly for ticks & remove them promptly. If you find a tick on your pet, save the tick with the date, or send it to a lab for immediate testing. Also get your pet tested, but keep in mind the pet may have a negative test & still have the disease if there are not enough antibodies in the pet’s serum to trigger a positive result. Watch closely for signs of sickness.
Canine Vaccine
A Lyme vaccine is available for dogs but it is not always recommended by veterinarians. While the vaccine causes more complications than other canine vaccines, the side effects are typically mild to moderate. The benefits of using the vaccine in endemic areas, especially for dogs with high exposure potential, far outweigh the risks.
Transmission
Pets show more serious symptoms of Lyme disease 2-5 months after the original tick bite. The symptoms typically include fever, joint swelling, difficulty walking, fatigue & loss of appetite.
Lyme nephritis affects 1-2% of dogs that develop clinical Lyme disease symptoms. This serious & almost always fatal complication is most often seen in labradors & golden retrievers. Given this additional risk, vaccination is even more imperative for these breeds.
Many dogs show a positive SNAP test for Lyme disease but are asymptomatic otherwise. In symptomatic cases, treatment consists of 28-30 days of antibiotics, usually doxycycline or amoxicillin. Symptoms can be alleviated quickly with antibiotic therapy but occasionally relapses occur.
Interactive Map from IDEXX Labs
Dogs get tested more regularly than humans for Lyme disease. Some researchers argue that the prevalence of Lyme disease can be more accurately inferred from the distribution of canine cases rather than from the human case maps compiled by the CDC. Here is an interactive map for Ehrlichia, Lyme disease, Heartworm, & Anaplasma cases reported to IDEXX Testing Labs from veterinary offices who test for these diseases across the United States. This map shows that Lyme disease is indeed in every part of the United States. Scroll down to the bottom of the map to change the disease results.

Pets can bring dangerous ticks into your home, & they also can suffer from tick-borne diseases.
Your Property
PROTECTING YOUR PROPERTY

Protecting your property is a vital step to reducing the risk of tick-borne diseases where you live. Full property protection does not remove the need for daily personal protection, as a person & pet can have ticks attached while off their own property; however, these solutions will significantly reduce ticks on your own property.
Use Tick Tubes to Kill Ticks on the Mice That Carry Them
Protect your property with tick tubes. Tick tubes are biodegradable cardboard tubes stuffed with cotton soaked in permethrin. Mice, which can each carry up to 100 ticks on their body, take the cotton from the tubes to their dens to use for nesting. The cotton does not harm the mice; however, it kills the ticks on the mice. Tick tubes are a huge contributor to reducing the number of ticks on your property. Watch our How-To Tick Tube video here.
Tick tubes work; tests have proven that the risk of encountering infected ticks on treated property can be reduced up to 97% by the use of tick tubes. Here, you can find information on how many you need for your property and how they work on this FAQ about tick tubes. You may make them yourself, or you may purchase them already made on the Internet. LymeTV has no affiliation with this company in the link, nor do we receive any money from them; we only provide the information as a convenience to learn more about tick tubes.
Stop Disease at the Source
Vaccinate the mice; integrative management solutions provide a comprehensive solution. Scientists from CT, NY, PA, & TN have developed an orally delivered vaccine that targets mice, the original host reservoir for Lyme & other tick-borne diseases. Non-infected mice cannot spread the infection to ticks. The vaccine technology has been tested for over 10 years. According to a study published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases (abstract), the authors demonstrated the vaccine pellet technology reduced the number of infected ticks by 76% in field conditions. Find out more on the USBiologic website here.
Create a Tick-safe Zone to Reduce Ticks in the Yard
Here are some simple landscaping techniques that can help reduce tick populations:
- Remove leaf litter.
- Clear tall grasses & brush around homes & at the edge of lawns.
- Place a 3-ft wide barrier of wood chips or gravel between lawns & wooded areas to restrict tick migration into recreational areas.
- Mow the lawn frequently.
- Keep playground equipment, decks, & patios away from yard edges & trees.
- Stack wood neatly & in a dry area (discourages rodents).
- Discourage unwelcome animals (such as deer, raccoons, & stray dogs) from entering your yard by constructing fences.
- Remove old furniture, mattresses, or trash from the yard that may give ticks a place to hide.
Apply Additional Pesticides Outdoors to Control Ticks
Use of acaricides (tick pesticides) can reduce the number of ticks in treated areas of your yard. However, you should not rely on spraying to reduce your risk of infection. If you have health concerns about applying acaricides:
- Check with local health or agricultural officials about the best time to apply acaricide in your area.
- Identify rules & regulations related to pesticide application on residential properties (Environmental Protection Agency & your state determine the availability of pesticides).
- Consider using a professional pesticide company to apply pesticides at your home.
Remove Japanese Barberry
This article from the University of Connecticut explains how eliminating the shrub will also help control the spread of tick-borne diseases.
Opossums
These animals eat approximately 5,000 ticks per season. How much of an impact opossums' eating ticks have on Lyme Disease infection rates is unknown; however, this study tested whether blacklegged ticks, the vectors of Lyme disease, granulocytic anaplasmosis & babesiosis can be regulated by the species of vertebrate hosts on which they obligately feed. By subjecting field-caught hosts to parasitism by larval blacklegged ticks, researchers found that some host species (e.g. opossums, squirrels) that are abundantly parasitized in nature kill 83–96% of the ticks that attempt to attach & feed on them. Opossums are not carriers of Lyme disease, nor rabies, making them an ideal & natural tick-control method.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- University of Connecticut

Tick tubes are just one way to prevent rodents from carrying ticks onto your property.
FAQs
COMMON QUESTIONS & MISCONCEPTIONS
Do I still need to worry about ticks with no deer around my home?
You do not need deer anywhere around you to have Lyme disease. This misconception is based on the name of a single tick species - the "deer tick." All black-legged ticks can transmit Lyme disease, & rodents (mice, chipmunks, & shrews) are the original hosts. Rodents are the main culprit; if you have mice where you live - which are in abundance in both urban & rural areas - you are at risk for Lyme disease. Areas with fields, leaf mulch, & trees naturally have more rodents, therefore more mice, therefore more Lyme disease. Lyme disease is in all 50 states of the U.S.A, & over 80 countries, worldwide.
When does Lyme disease turn late stage?
Lyme disease starts to disseminate throughout the host body at around 4-6 weeks after infection. At this point, it starts heading into stage 2 of the disease. Basically, when certain late-stage symptoms emerge, Lyme disease has progressed & may be considered late stage. Timelines can vary on a case-by-case basis. For instance, a person may have neurological manifestations early after infection, & this may be considered late stage; whereas another person may have Lyme disease undiagnosed for many years (definitely considered late-stage) & it could possibly never present neurologically.
How do ticks get infected with Lyme disease?
Ticks are vectors (carriers which transmit) of the bacteria that causes Lyme disease. They also carry many other very dangerous & deadly tick-borne diseases. They get infected when they feed on other animals, mainly rodents. Ticks feed on birds, reptiles, amphibians, & mammals. Once the tick is infected from feeding on the host animal, it then can spread the disease(s) it carries to the next animal it feeds upon.
Do all ticks carry Lyme disease?
No; a tick must first feed on an infected animal to become a carrier of the disease. But there is no way of knowing if a tick is infected just by looking at it. If you ever find one on your body, save it with the date found for testing or send it immediately to a tick testing lab for analysis.
I heard stevia kills Lyme disease. Is this true?
No; this is not true at all. The laboratory study, which has been misrepresented by popular media, only shows that the stevia extract can kill the bacteria IN VITRO (not in human bodies). Why does this matter? The research did not claim that stevia was an effective clinical cure but a potentially promising chemical pathway that warranted further investigation into whether some derivative from stevia whole leaf extract could be made into an effective medication.
The study demonstrated the antimicrobial properties of stevia whole leaf extract, which has many active chemical agents, & should not be confused with the purified sweetener that is sold as a sugar substitute in grocery stores. There is no evidence that the stevia extract can replicate killing the bacteria in the human body. Most compounds that are effective in vitro fail to progress to medications that work in the human environment. You can find the original study here.
Can I remove ticks with peppermint oil?
If you see a tick on you, you want to get it off fast. You should always remove an attached tick with tweezers. Waiting several seconds or minutes to see if a tick will detach itself while it could be transmitting dangerous infections is not safe. Putting oil on an attached tick may also agitate the tick, which can increase the risk of tick-borne diseases to be transmitted. Find more information on this topic in this article.
Who is most likely to get tick-borne infectious diseases?
Anybody is susceptible to getting a tick-borne disease; however, the people who get it the most are children because they play more outside. Ticks do not care about your age, sex, or nationality to want to feed on you. Ticks are parasites & will feed on any mammal, bird, amphibian, & reptile to survive.
Do ticks die in the winter?
No; ticks survive winter. They hibernate under 35 degree Fahrenheit (around 1.6 Celsius), & come out to feed when the ground is thawed & the temperatures are above freezing. Wearing protective clothing & doing tick checks on these warmer winter days can greatly reduce your winter risk of transmission.
How long do ticks live?
A tick's life-cycle is 2 (or more) years. They have 4 stages of life (egg, larva, nymph, & adult). Ticks must feed in each stage of the life cycle to survive & mature to the next stage of life.
What should I do with a tick if I find one on me?
It is important to know how to properly remove a tick. By squeezing the body of a tick during removal, you may push the blood from the engorged tick back into your body, which can cause a greater risk of disease transmission. When you find a tick on you, always save it in a bag with the date it was found. You have the option of sending it to a tick lab for testing or waiting to see if you present with clinical symptoms before getting it tested. Keep in mind that disease(s) may be disseminated in your body & turn late-stage long before you get properly diagnosed. Be aware of clinical symptoms & get on antibiotics immediately if you get a bulls-eye rash.
Where is Lyme disease prevalent?
Lyme disease is in all 50 states of the U.S.A, & in over 80 countries, worldwide. While Lyme disease may not be equally prevalent in all of the states, there are many other very dangerous tick-borne diseases in those regions. Do not think that you cannot get Lyme disease because you are not in the northeastern or midwestern regions of the U.S.A, where the highest incidence occurs. That would be a false sense of security.
Where are ticks located?
Ticks are everywhere, & there are over 800 species globally. Many species can spread a multitude of very dangerous & deadly tick-borne diseases. Ticks like to ward off dehydration by hiding under leaf mulch. Ticks also can be found in high grass, where trees meet the lawn, near wood piles, & more.

Misconceptions debunked & other information.
One Tick Bite Can Spread Multiple Diseases
A single tick bite can transmit many pathogens, causing serious illness.
Tick diseases spread at different rates, so a tick attached for any amount of time can be a potential risk. Testing the tick can determine the diseases it might have.
What You Need To Know
It is vital to recognize the symptoms & get treatment early.
Diagnosis with co-infections also complicates the choice of treatment protocol, as different co-infections require other specific antibiotics or other types of medications.

Clinical Research Studies Seeking Participants
Ongoing studies help research evolve.
You can contribute to research by signing up as a volunteer in clinical trials or donating blood, urine, or tissue samples to a bio bank.
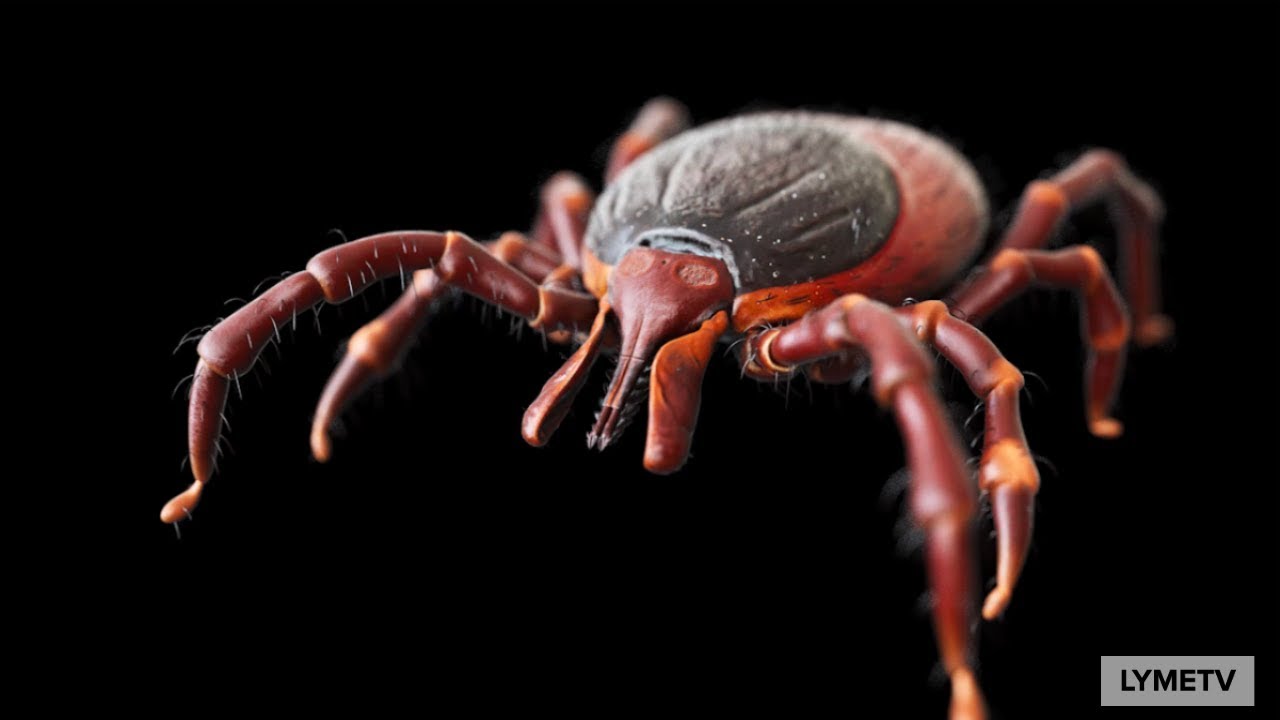

Free Tick Bite Prevention Resources
Tick bite prevention education is key to reducing incidence of tick-transmitted pathogens.
LymeTV provides free age-appropriate health education resources for adults & youth. Materials are available in multiple languages.
